
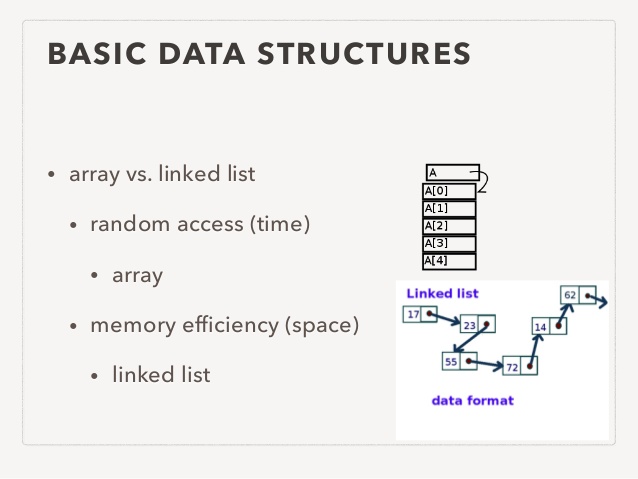
JSR note: Note that trees are only a Topic 5, not an Option topic.ĥ.1.14 Describe how trees operate logically (both binary and non-binary).ĥ.1.15 Define the terms: parent, left-child, right-child, subtree, root and leaf.ĥ.1.16 (MOVED to Recursion Page) State the result of inorder, postorder and preorder tree traversal.ĥ.1.17 Sketch binary trees. Tracing and constructing algorithms are not expected. Students are not expected to construct tree algorithms using pseudocode. Once again, remember Topic 5, gnerally is to be "examined at the level of diagrams and pseudocode."Ĭode-Camp-Day-1: Stacks and Queues Implemented (YT)ĥ.1.6 Describe the characteristics and applications of a stack.ĥ.1.7 Construct algorithms using the access methods of a stack.ĥ.1.8 Describe the characteristics and applications of a queue.ĥ.1.9 Construct algorithms using the access methods of a queue.ĥ.1.10 Explain the use of arrays as static stacks and queues.īinary trees will be examined at the level of diagrams and descriptions. JSR Note: But for Option D, you are expected to construct and use Java algorithms using the LinkedList ADT.ĥ.1.13 Sketch linked lists (single, double and circular).

Students are not expected to construct linked list algorithms using pseudocode. Linked lists will be examined at the level of diagrams and descriptions. (JSR added - it helps the understanding of dynamic data structures.)ĥ.1.12 Describe how linked lists operate logically.
#Linked list stack java questions csci quiz license
Great college level open source license textbook to aid you.įor 5.1.1 - 5.1.3, refer to Topic 5 & OOP Recursion main section.ĥ.1.4 Describe the characteristics of a two-dimensional array.ĥ.1.5 Construct algorithms using two-dimensional arrays.ĥ.1.18 Define the term dynamic data structure.ĥ.1.11 Describe the features and characteristics of a dynamic data structure (like linked list)ĭ.4.5 - Define the term object reference. Each basic idea should then be practised in specific algorithmic contexts using concepts drawn from flow charts, pseudocode and programming.Įxtra resource: Java, Java, Java by Ralph Morelli & Ralph Walde. The basic ideas and their application should be illustrated with non-computer examples. This should be taught and connected to flow charts, pseudocode and programming in the SL/HL core. Students should be able to describe the most common data structures (arrays, stacks, queues, linked lists, binary trees) and the most common data processing operations on each of the basic data structures (addition, deletion and retrieval of data, traversal, searching for a given data, sorting of data into some order).

This will be examined at the level of diagrams and pseudocode. HL extension (45 hours) Topic 5- Abstract data structures (23 hours) 5.1 Abstract data structures (23 hours)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
